The human immune system typically makes large numbers of antibodies and lymphocytes. The antibodies and lymphocytes help fight off infections.
The immune system does not attack normal cells in the body. But in autoimmune disorders, the immune system produces antibodies and lymphocytes, referred to as autoantibodies that target the body’s cells and tissues.
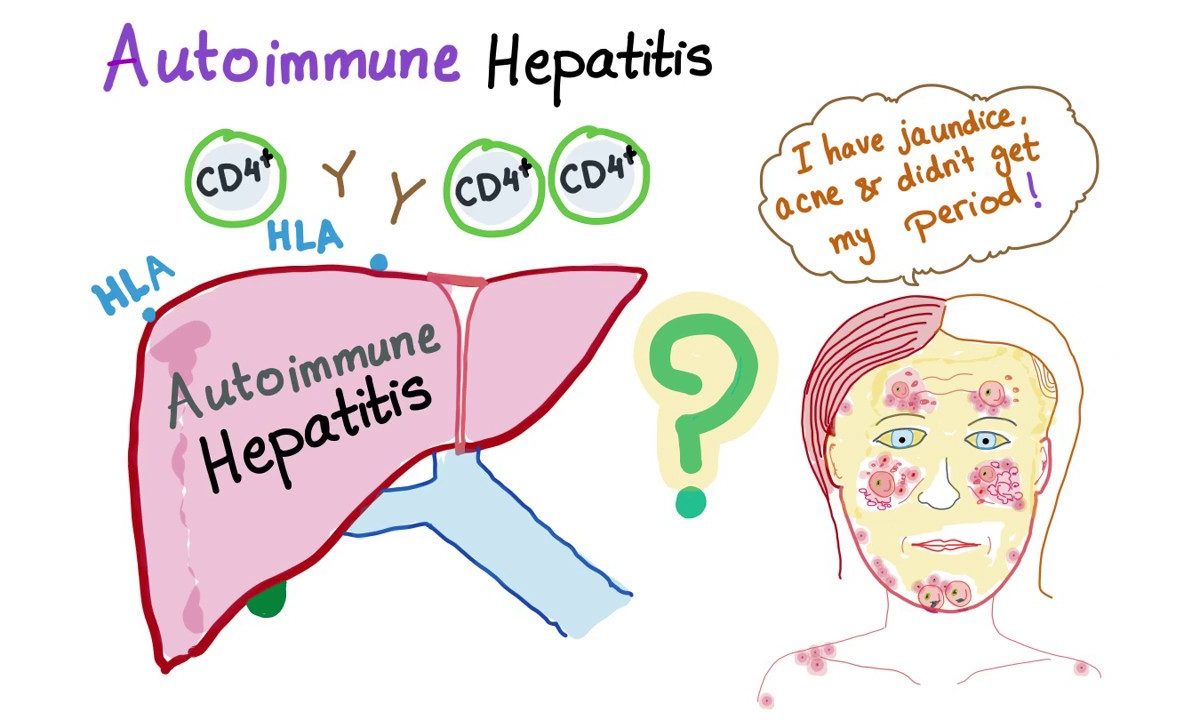
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic condition in which the immune system targets the liver. It results in inflammation and damage to the organ. If left untreated, autoimmune hepatitis will deteriorate. It will lead to complications, including cirrhosis and liver failure.
Now, let’s know more about autoimmune hepatitis, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and autoimmune hepatitis treatment.
What is Autoimmune Hepatitis?
In autoimmune hepatitis, the body’s innate immune system destroys the liver’s cells. It causes inflammation and liver damage. It is a long-term illness. The autoimmune system will lead to cirrhosis and liver failure if left unchecked. Autoimmune hepatitis affects over a million people and leads to a Liver transplant in India. The majority of those affected are between the ages of 14 and 40.
- Liver failure– happens when the liver stops functioning.
- Cirrhosis– occurs as scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue, obstructing natural blood flow.
Types of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Type 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis:
It is the most common disease. Around half of those with autoimmune hepatitis may have rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, or ulcerative colitis.
Type 2 Autoimmune Hepatitis:
Adults are more likely to contract this form of hepatitis. However, it is most prevalent among infants and teenagers. Other autoimmune disorders can also accompany this form of illness.
What are the symptoms of Autoimmune Hepatitis?
Symptoms differ from person to person. The following are some of the common symptoms:
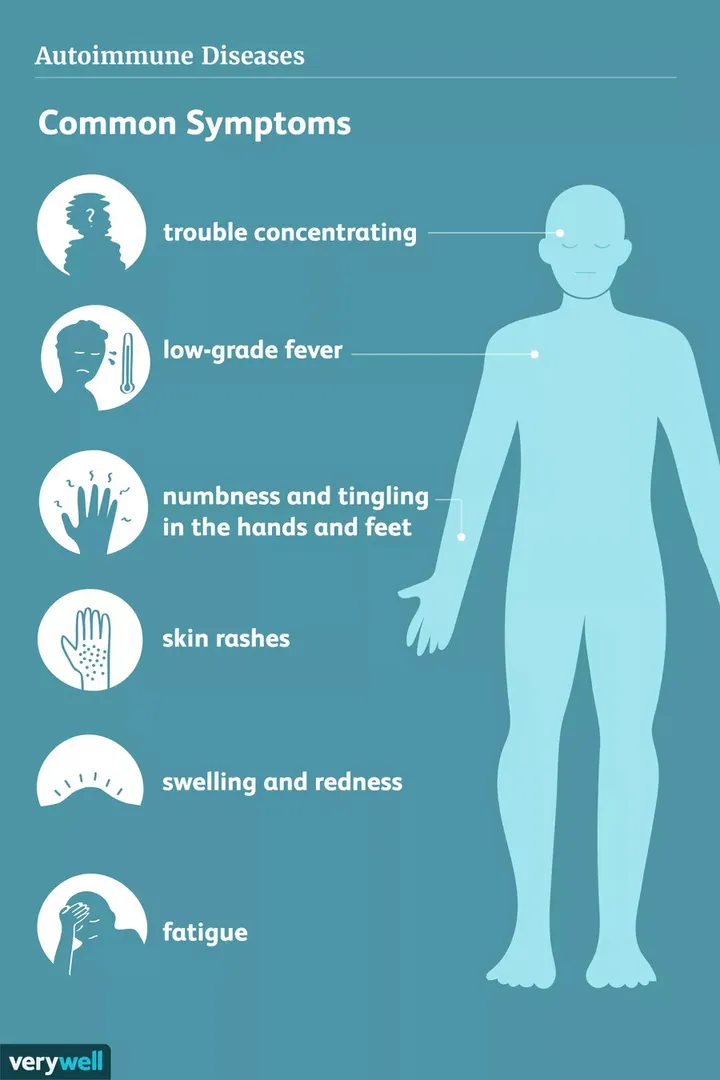
- Excessive fatigue
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Abdominal pain
- Itching
- Joint pain or swelling
- Mild fever
- Spiderlike blood vessels in the skin
- Large abdomen due to enlarged liver and spleen
The symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis will mimic those of other illnesses. Therefore, always seek medical advice for a diagnosis.
Patients can suffer from problems such as permanent scarring of the liver tissue. Other conditions that could arise are:
- Liver failure
- Fluid collection in the abdomen
- Enlargement of the veins of the esophagus
- Liver cancer
What Causes Autoimmune Hepatitis?
The immune system attacking liver cells is the most common cause of autoimmune hepatitis. However, the reason for the body’s self-attack on the liver is unclear. Researchers believe it is due to a genetic interaction.
Following other risk factors can raise the risk of getting autoimmune hepatitis:
- Gender – Females are more likely to have autoimmune hepatitis than males.
- Infections – Infections such as influenza, herpes simplex, or the Epstein-Barr virus increase the risk of acquiring autoimmune hepatitis.
- Heredity – People with a family history of autoimmune hepatitis are at a higher risk of contracting the disease.
How is Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosed?
A physician would diagnose the cause of autoimmune hepatitis by understanding the patient’s symptoms, performing a physical examination, blood tests, and liver biopsy.
- Blood tests – It distinguishes autoimmune hepatitis from other liver disorders with similar symptoms, such as viral hepatitis.
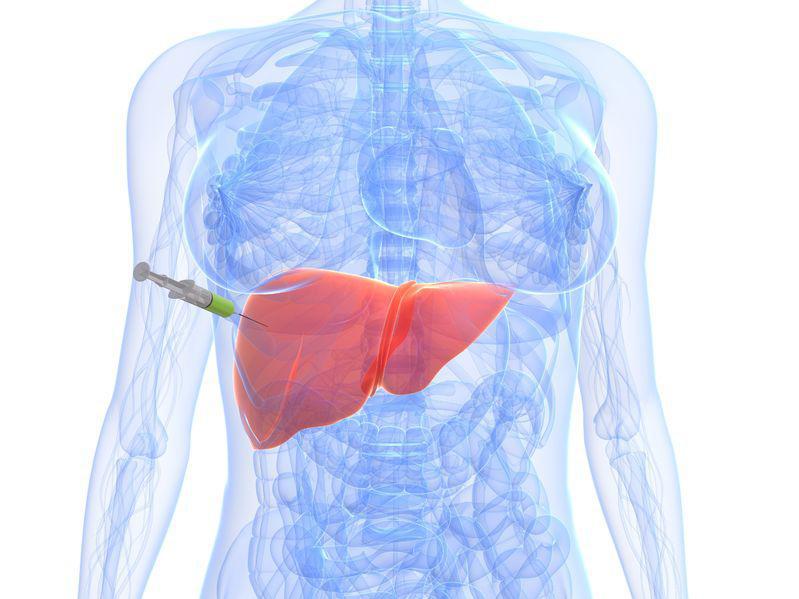
- Liver biopsy – A liver biopsy determines the degree and type of liver tissue damage. It involves inserting a needle across the skin to the liver, removing a small sample of liver tissue, and examining it under a microscope for the presence of any diseases.
Presentation Of Auto-Immune Hepatitis: Generally Autoimmune hepatitis presents as a slow or chronic disease. Sometimes it will present as Acute Liver Failure. If it presents as Acute Liver Failure, Liver Transplant remains the only Life-saving option.
Autoimmune Hepatitis Treatment
The main goal of autoimmune hepatitis treatment is to suppress the overactive immune system. In most patients, the disease can be managed by following the standard treatment options.
- Medications – They are the first preference of treatment. If the symptoms are mild or there are no symptoms, the doctor may not prescribe any medicines. Corticosteroids help reduce swelling and decrease the immune system’s activity. The main task is to find the lowest dose sufficient to treat the disease.
- Immunity suppressors – These drugs reduce inflammation and block the immune cell’s activity.
- Liver transplant – In most severe cases, such as cirrhosis or end-stage liver failure, a transplant is required. A healthy donor’s liver would then replace the liver.
How People Live with Autoimmune Hepatitis?
- With treatment, most patients with autoimmune hepatitis can have an average life expectancy. The medication used for autoimmune hepatitis has improved the chances of survival tremendously. The patient should not stop the treatment without the doctor’s knowledge, as the condition may worsen.
- Although the condition usually deteriorates at some point after stopping treatment, it can generally be treated again by quickly going back on medication.
Make an appointment with Dr. Gaurav Gupta to seek the most effective Autoimmune hepatitis treatment in Mumbai.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1) What is the survival rate for Autoimmune Hepatitis Patients?
Generally, Auto-Immune Hepatitis patients will have a normal life. Sometimes it presents as Acute Liver Failure where urgent liver transplant may be required.
2) Is there a difference between Autoimmune Hepatitis and Viral Hepatitis?
Autoimmune hepatitis is an immune disease caused by genetic causes, while viral Hepatitis is a viral infectious disease. They can be Hepatitis A, B,C, E
3) Does Autoimmune Hepatitis impact fertility or conception?
Autoimmune hepatitis does not affect pregnancy. Women of childbearing age with autoimmune hepatitis can conceive without any difficulty. However, for healthy childbirth, it is best to follow the doctor’s instructions.