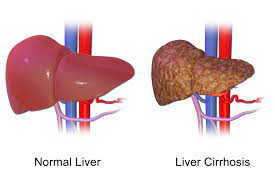
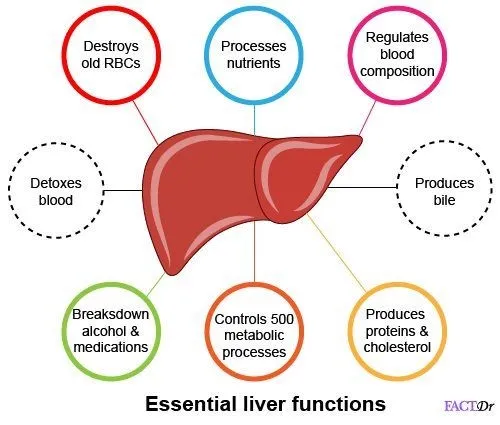
Our liver has the ability to repair and regenerate itself. However, as it gradually builds scar tissue, it is less able to function correctly. As the number of scarring increases, the liver’s circulatory flow decreases. Further, the essential functions of the liver are compromised. In some cases, this may lead to liver failure and even death. Globally, over one million people die every year from Cirrhosis.
Dr. Gaurav Gupta, Head of Liver Transplant and HPB Surgery at Fortis Hospitals, Mumbai has over decades of experience in handling complex liver surgeries and treatment of Liver Cirrhosis too. Due to his vast expertise and experience, he is known to provide the best liver transplant in Mumbai.
Now, let’s know about Cirrhosis, its diagnosis, and treatment.
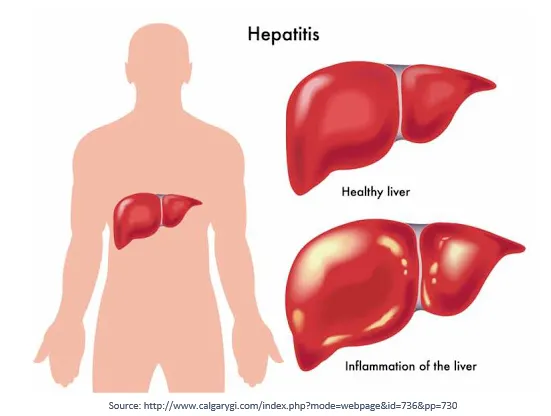
Prolonged liver damage leads to a condition known as Cirrhosis of the liver. In this condition, the liver becomes hard and nodular. Liver tissue is replaced by fibrosis. Once cirrhosis sets in, liver damage becomes irreversible. The cirrhotic liver becomes incapable of regenerating.
Classification of Cirrhosis
1. Compensated Cirrhosis
It is merely a damaged liver that is still relatively functional.
2. Decompensated Cirrhosis
It represents the advanced stage of cirrhosis where signs and symptoms of liver dysfunction start.
Why can Cirrhosis be Dangerous?
Cirrhosis leads to various complication like
- Ascites (fluid in the abdomen)
- Edema (fluid in limbs)
- Variceal bleeding (bloody vomiting)
- Confusion (encephalopathy)
- Kidney dysfunction (hepatorenal Syndrome)
- Lung complication (Hepatic hydrothorax, Hepatopulmonary syndrome)
- Liver cancer
The risk of death with intractable ascites and variceal bleed can be quite high. Patients with ascites that are not controlled with medications (intractable ascites) have a mortality risk of almost 70% within one year.
A single episode of infection in patients with ascites (SBP) carries a 50% one-year mortality risk.
If complications are not controlled when the liver ceases to function, your Liver Transplant Surgeon in Mumbai may recommend liver transplantation.
Approximately 5% of people with cirrhosis develop hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It’s the most common form of liver cancer.
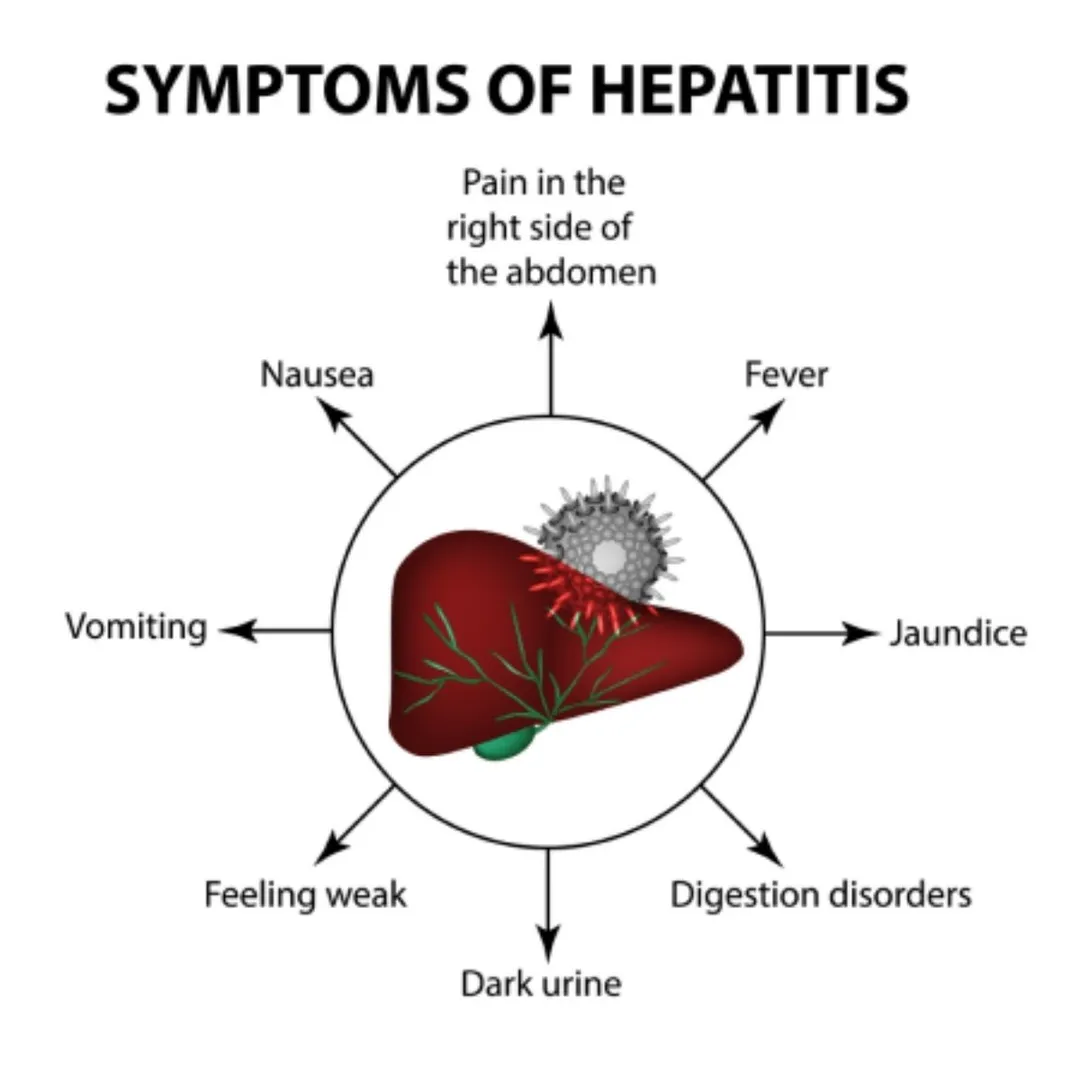
Symptoms of Cirrhosis
Progression of liver damage from early-stage fibrosis to cirrhosis usually takes years to manifest symptomatically. There are often few, if any, symptoms in the early years.
When symptoms occur, they are sometimes misdiagnosed, ignored, or attributed to other possible causes. However, as the ailment progresses, the symptoms may get more apparent. These symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Confusion
- Weakness
- Itching
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Nausea
- Easy bruising
- Jaundice
- Swelling of ankles, feet, and legs
- Abdominal bloating from the ascites
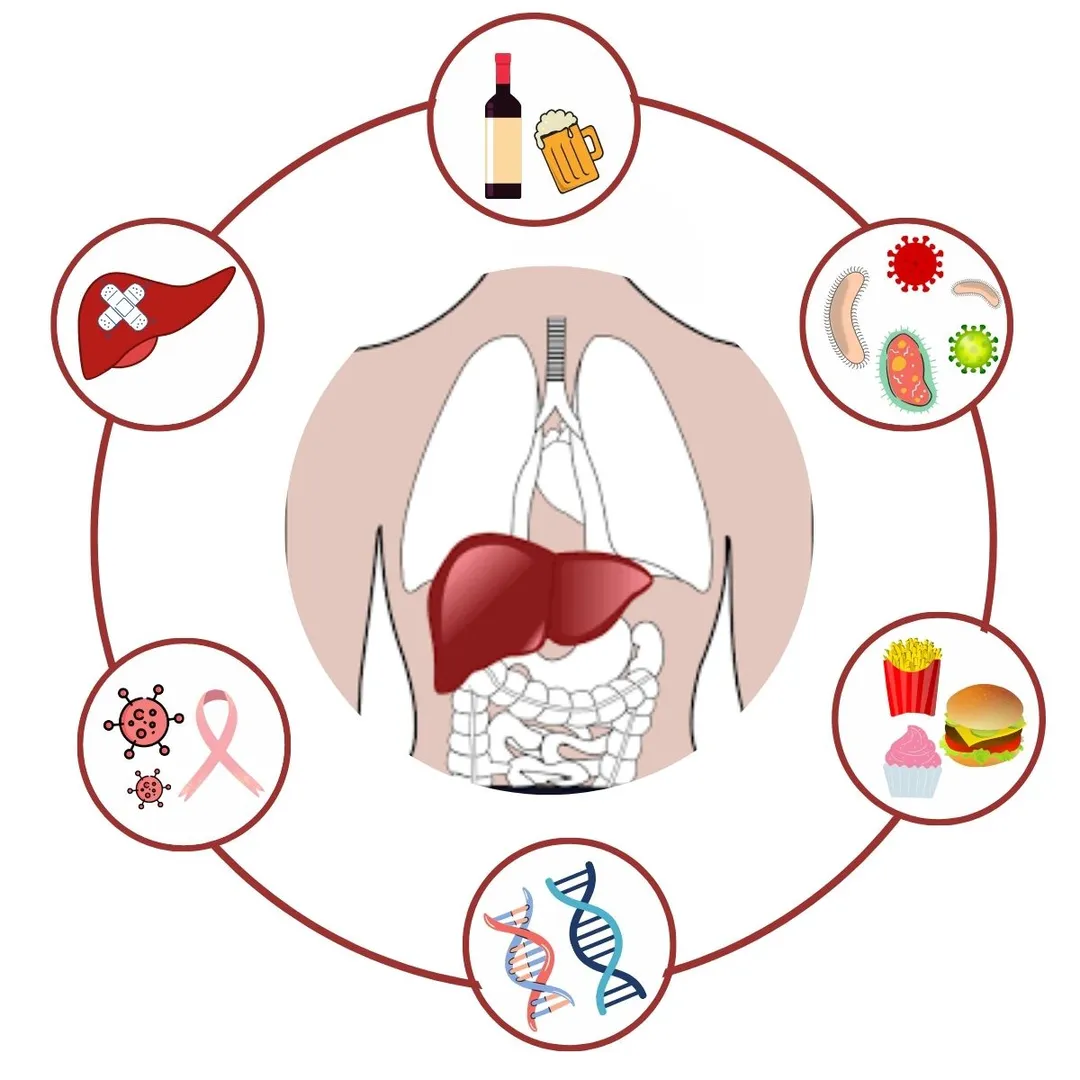
Causes of Cirrhosis
The most common causes of cirrhosis are:
- Alcohol-related liver disease: It is typically associated with heavy alcohol intake over several years.
- Hepatitis B: It is a prevalent cause of cirrhosis.
- Hepatitis C: It is one of the frequent causes of cirrhosis and the leading indicator for liver transplants.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: People with diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, and high cholesterol are more prone to cirrhosis. This is becoming one of the most common causes of Liver cirrhosis with the increasing incidence of lifestyle diseases in our population.
Some of the rare causes of cirrhosis include:
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
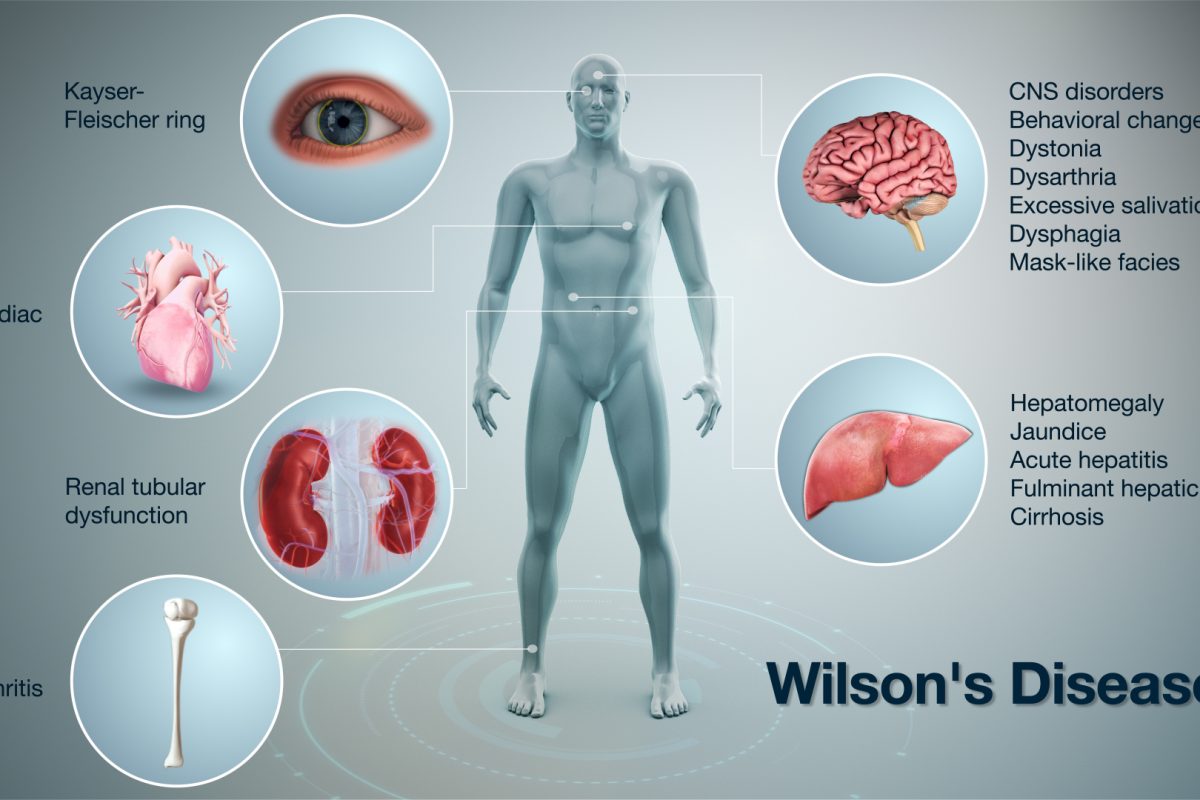
- Hereditary diseases like Wilson’s disease
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Hemochromatosis
- Celiac disease
- Medication
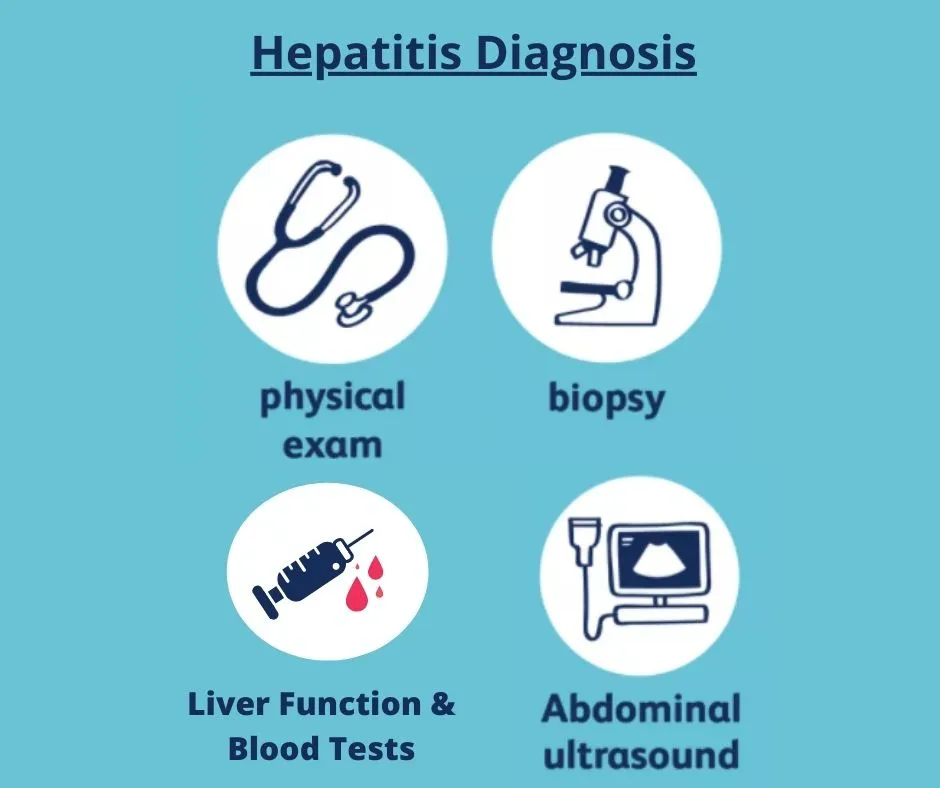
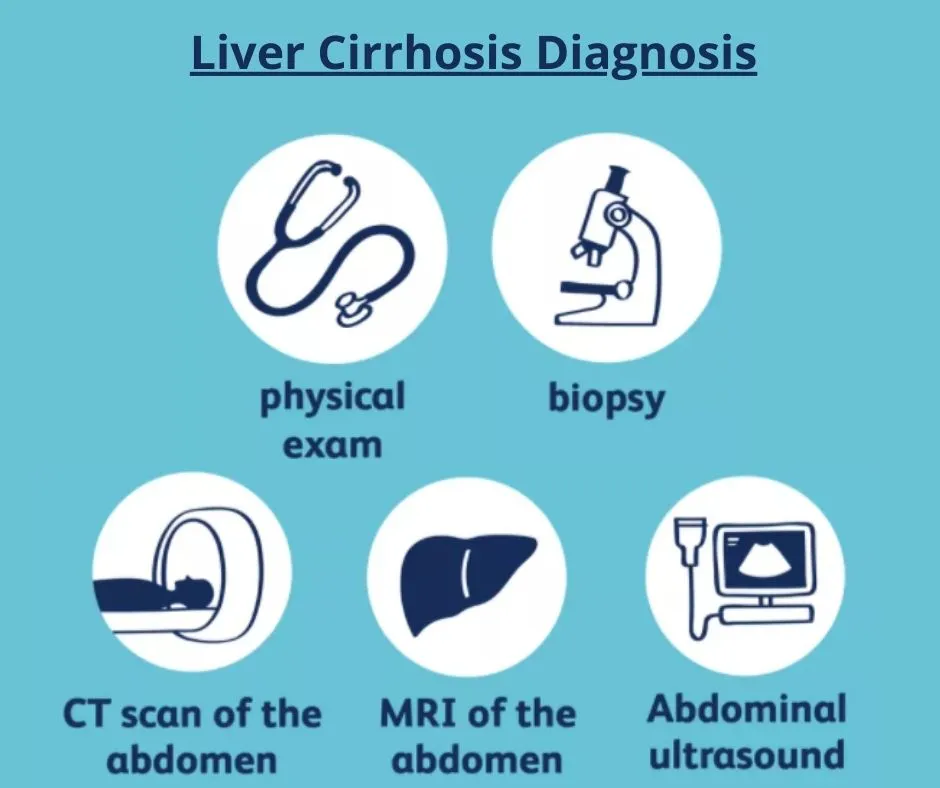
Diagnosis of Cirrhosis
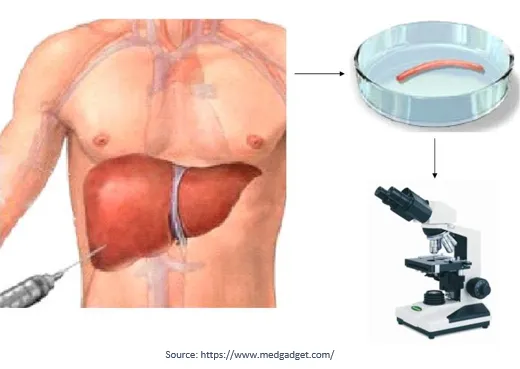
1. Liver biopsy:
It is the most accurate method for the diagnosis of cirrhosis and its stage. With advancements in Radiological tools, Liver Biopsy is rarely done these days to diagnose cirrhosis.
2. An ultrasound or Magnetic Resonance Elastography:
These are non-invasive ways to detect cirrhosis.
3. Blood tests and imaging tools (CT scan and MRI):
These can be used to monitor disease progression.
Treatment of Liver Cirrhosis
- Many cases of cirrhosis have been manageable before they progress and require a liver transplant in Mumbai.
- The management of cirrhosis depends primarily on the cause and severity of the disease.
- But the treatment should begin immediately after its diagnosis.
- Cirrhosis is generally not curable except through liver transplantation.
You should take the below steps to decrease the progression of liver scarring, including:
- Avoid taking alcohol and medicines that can cause injury to the liver.
- Avoid over-the-counter herbal agents and supplements, as some have been associated with liver injury.
- Cirrhosis elevates the risk of prescription-drug liver injury. So, all prescriptions should be carefully reviewed for effects on the liver.
- Avoid raw shellfish that may contain bacteria. It could potentially cause severe infection in people with advanced liver disease.
- Screening and vaccination for hepatitis A and hepatitis B
- Antiviral therapy for hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
- Screening and treatment of secondary causes of cirrhosis such as ursodiol for bile duct blockages.
- Nutrition plays an important role in managing Cirrhosis patients.
The management of cirrhosis should begin as soon as you’re diagnosed with the condition. After the diagnosis, you should always consult a qualified and experienced Liver Specialist in Mumbai to seek the best treatment.